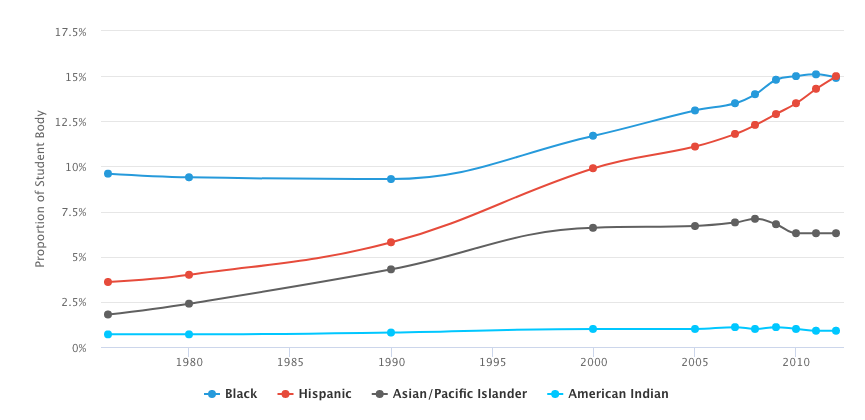
College enrollment rates are rising among Hispanic men and women in the United States. Recent data from the Pew Research Center shows that 2.2 million Hispanics between the ages of 18 and 24 were enrolled in a two-year or four-year degree program in 2015; this figure represents a threefold increase since 1993. This rise in postsecondary attendance is largely attributable to the nation’s growing Hispanic population and a sharp decline in the high school dropout rate among this demographic. According to the National Center of Education Statistics (NCES), the percentage of college students who identify as Hispanic rose from 4% to 15% between 1976 and 2012. Hispanic students reached a new milestone in 2012 when, for the first time, Hispanic high school graduates enrolled in college at a higher rate than their Caucasian counterparts. The U.S. Census Bureau estimates one in four college students will identify as Hispanic by 2020.
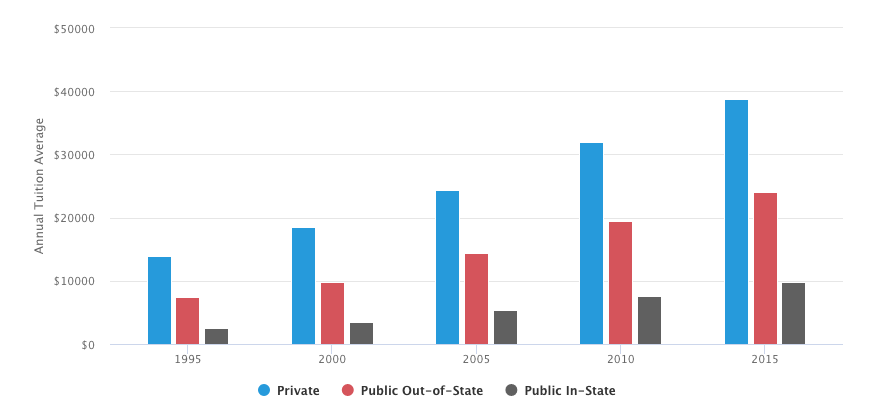
Persistent educational challenges continue to affect the Hispanic community, however. Many college-bound Hispanic men and women come from low-income families, and tuition rates for in-state students at public universities have risen 296% over the past 20 years. Consequently, many of these students are forced to absorb student loans to afford their degree. These loans carry steep monthly minimum payments and interest rates that can affect borrowers for decades.
Unique Challenges
Pew Research data shows that 22% of Hispanic students have outstanding student debt. While this is the lowest rate of debt among student racial groups, it should be noted that nearly half of all Hispanic students complete their education at a two-year community or technical college. These programs tend to be significantly less expensive than four-year programs, but they are also less likely to help students secure meaningful post-college employment. As of 2015, only 15% of Hispanics aged 25 to 29 held a bachelor’s degree in any subject.
FAMILY NEEDS
Family obligations present another challenge to Hispanic learners. A 2015 survey by the National Journal found that two-thirds of Hispanic men and women who sought full-time work or joined the military after high school claimed to have done so in order to financially support their loved ones. By comparison, only 39% of white men and women who bypassed college made the same claim.
FIRST-GENERATION COLLEGE STUDENTS
First-generation Hispanic college students face additional obstacles. The percentage of first-generation students at all U.S. postsecondary four-year institutions fell from 38.5% to below 16% between 1971 and 2005, according to a report from UCLA. A study by the National Conference of State Legislatures (NCSL) further estimates that up to half of Latino parents have not received any postsecondary education. Many educational experts agree that parents without a college background are unable to fully prepare their children for the rigorous academics and the social pressures of institutionalized higher education. “Without family background in the college experience,” the study notes, “these students may find it difficult to fully engage in college life, which can lead them to drop out and not complete a degree.”
ENGLISH AS A SECOND LANGUAGE
Language barriers are another factor. Hispanics made up 46% of all U.S. immigrants in 2013, according to data from the Migration Policy Institute, and the National Education Association (NEA) notes that roughly 80% of the country’s English Language Learners (ELLs) identify as Hispanic. Despite a widespread emphasis on English instruction in U.S. public schools, however, less than 20% of k-12 ELL students earn average or above-average reading comprehension scores. Furthermore, up to 10% of ELL students between the ages of 12 and 18 are forced to repeat a grade every year. The lack of English speakers in the home is a major reason for these trends.
CHILDREN OF MIGRANT WORKERS
Another underrepresented group are the children of Hispanic migrant workers. Each year, the U.S. Department of Education’s Migrant Education Program serves approximately 345,000 Hispanic students between the ages of three and 21. The College Assistance Migrant Program (CAMP) offers financial support for college freshmen, along with five-year tuition grants, but because migrant families are constantly on the move, these students often perform poorly in the classroom and their secondary school dropout rates are higher than non-migrant students.

Financial Aid for Undocumented Students
Roughly 65,000 undocumented students graduate from U.S. high schools each year. The U.S. Department of Education guarantees public education for undocumented children through grade 12. Additionally, there are no federal or state laws prohibiting undocumented men and women from applyng to, enrolling in, and graduating from public or private colleges. A survey by the National Association of Student Financial Aid Administrators (NASFAA) found that 32% of public postsecondary institutions admitted undocumented student applicants.
However, many schools categorize undocumented students as “foreign”, thus making them ineligible for both federal financial aid and in-state reduced tuition rates. The Obama administration has introduced a bill known as the Development, Relief, and Education for Alien Minors (DREAM) Act that would create a college pathway for undocumented students by providing them with permanent residency. However, the DREAM Act has yet to receive congressional approval as of April, 2016.
DEFERRED ACTION FOR CHILDHOOD ARRIVALS
Students in the U.S. must be permanent residents before they can receive federal financial aid. Most immigrants earn permanent residency by applying for a Green Card, but current laws stipulate that undocumented citizens are unable to take this path; they must instead leave the United States and apply for permanent residency from a consulate office in their home country.
The Deferred Action for Childhood Arrivals program, or DACA, seeks to ease college admission challenges for undocumented students. Under DACA, undocumented children who enter the U.S. prior to age 16 receive “deferred action status” and are categorized as DACA Students. They may also be able to obtain a social security number (SSN). While DACA students are still ineligible for federal financial aid, those with a valid SSN are able to fill out a Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) and they may receive state- or institution-sponsored funding.
DACA students may also qualify for reduced in-state tuition, although discounted rates are often available. A total of 18 U.S. states currently offer provisions for undocumented students to receive discounted in-state tuition. These include: California, Colorado, Connecticut, Florida, Hawaii, Illinois, Kansas, Maryland, Michigan, Minnesota, Nebraska, New Mexico, New York, Oklahoma, Oregon, Rhode Island, Texas, Utah, and Washington. In contrast, three states have barred reduced in-state tuition for undocumented students: Arizona, Georgia, and Indiana. The remaining 29 states are classified as unstipulated.
Undocumented students should meet with their high school career counselor to discuss financial aid options for college. Most DACA students with a valid SSN are urged to complete a FAFSA in order to learn about state- and institution-based financial aid options. The Department of Education offers the following tips for DACA students who wish to fill out a FAFSA:
HOW TO FILL OUT THE FAFSA AS AN UNDOCUMENTED STUDENT
-
The FAFSA does account for the citizenship status of the applicant’s parents, but the form requests the SSNs of both parents. Applicants must write in 000-00-0000 for the SSN for any undocumented parent or legal guardian.
-
Applicants will encounter the following question: “Are you a U.S. citizen?” Undocumented students must check the box for “No, I am not a citizen or eligible noncitizen.”
-
There are also questions inquiring about the “legal state of residence” for the applicant and their parents. The correct answer will vary, as each U.S. state has different requirements for legal state residency. Applicants should consult their on-campus career counselor before completing this section.
-
The online FAFSA form features an IRS Data Retrieval tool that allows applicants to submit their tax information and their parents’ tax information. If the applicant or their parents did not file an income tax return during the previous year, then tax information may be entered manually.
HISPANIC-SERVING INSTITUTIONS
The Hispanic-Serving Institutions (HSI) program was enacted through Title V of the Higher Education Act. HSI status is conferred on not-for-profit postsecondary institutions where at least 25% of full-time students identify as Hispanic. Under Title V, eligible HSIs can receive grants from the U.S. Department of Education’s Office of Postsecondary Education (OPE). Grant funding is then used to build on-campus resources and bolster support services for Hispanic students. Today, HSIs are represented by the Hispanic Association of Colleges & Universities (HACU); although HACU members comprise only 10% of U.S. postsecondary institutions, these colleges and universities are home to more than two-thirds of the nation’s Hispanic student population.
The rising number of HSIs in the U.S. directly correlates with the increasing number of Hispanic students enrolling in accredited college programs. There were 245 recognized HSIs in 2005, and as of 2014-15, there were 435 recognized HSIs that collectively enrolled more than 1.8 million students. The states with the most HSIs are California with 152, Texas with 78, Florida with 24, and New Mexico with 23. Additionally, Puerto Rico has 63 recognized HSIs.
Scholarship Basics
 A scholarship is a monetary gift for students to use for funding their postsecondary education. Scholarships do not need to be paid back, making them a desirable alternative to student loans. Scholarships may be used to pay for education-related costs including tuition, books, and other course materials. Some scholarships may also be used to cover food, room-and-board, laundry, and day-to-day expenses.
A scholarship is a monetary gift for students to use for funding their postsecondary education. Scholarships do not need to be paid back, making them a desirable alternative to student loans. Scholarships may be used to pay for education-related costs including tuition, books, and other course materials. Some scholarships may also be used to cover food, room-and-board, laundry, and day-to-day expenses.
Thousands of different scholarships are available. Merit-based scholarships are typically given to students with high GPAs or an extensive record of community service. Other scholarships may be allotted to certain groups of people, including women or minority students. There are also scholarship options for students who demonstrate financial need.
In order to qualify for most scholarships, students must first complete an application. While the nature of these applications will vary by award, most will include the following general criteria:
- Grades/Transcripts: Most scholarships (merit- and non-merit-based) require a minimum GPA for consideration; this minimum is usually 2.5 or higher. Additionally, some impose minimum scores on the SAT, ACT, or other college admissions tests.
- Essay: Many scholarships require applicants to complete an original written testimonial explaining why they deserve the award.
- Letters of Recommendation: A scholarship application may ask for letters of recommendation from teachers, school counselors, former employers, and other people who have interacted with the student in an educational or professional environment. These letters should not come from friends, relatives, or family acquaintances.
- College Information: Many scholarships will only award money to applicants who have enrolled or plan to enroll in an accredited postsecondary institution within the following year. Some are only allotted to students who plan to pursue certain fields of study.
- Other Financial Aid: For needs-based scholarships, applicants may need to prove they are not receiving federal financial aid, additional scholarships, grants, or other forms of monetary support.
HERE ARE A FEW EXPERT PIECES OF ADVICE FOR FILLING OUT SCHOLARSHIP FORMS:
- Begin your scholarship search during your freshman year of high school and compile an organized, comprehensive list of options before your senior year. Earning scholarship funding is essentially a numbers game; the more scholarships you apply to, the more financial support you’re likely to receive.
- Apply to every scholarship award for which you are eligible. Smaller scholarships are generally less competitive, and these awards can increase your overall support.
- Fill out all applications in pencil and be sure to proofread each section for misspelled words, grammatical errors, and awkward phrasing.
- Essays should be personal and heartfelt. Applicants should take this opportunity to demonstrate their writing skills and speak directly to the scholarship committee; be as expressive and direct as possible.
- If an online option is unavailable, submit your application to the scholarship committee by direct mail. In either case, be sure to keep a copy for your records in case the original application is not received.
- Be mindful of deadlines and make sure every application has been finished and submitted before its due date.
EXTERNAL SCHOLARSHIP RESOURCES
Students who are unfamiliar with scholarship applications should seek advice from educational experts. Here are a few online resources for scholarship applicants to peruse:
QuestBridge: This organization provides assistance and support to low-income and underprivileged men and women with college aspirations. QuestBridge’s website features links to more than a dozen scholarship databases.
FastWeb!: This comprehensive financial aid database allows users to customize scholarship criteria in order to generate a list of applicable awards.
ScholarshipAmerica.com: This organization “works to engage private sector support for programs and policies that advance equity in postsecondary education.” Their site links to 15 government-sponsored and private financial aid databases.
CareerInfo.net: The scholarship aggregator on this U.S. government-sponsored site lets users customize scholarship options by award type, education level, state of residence, and award sponsor.
BigFuture: CollegeBoard’s customizable scholarship aggregator allows users to browse more than 2,200 scholarships, internships, and other financial aid opportunities.
Some of the most common scholarships include:
Colleges and Universities: Most postsecondary institutions offer scholarships to current and prospective undergraduate and graduate students. Many scholarships are specific to major fields of study or offered exclusively to students in certain gender or minority groups.
Foundations: Students should explore scholarship opportunities through established businesses and professional organizations affiliated with their proposed field of study. Other foundational awards are available through women’s or minority rights advocacy groups.
Local Community Organizations: Scholarships are often offered through community-based groups such as churches, youth centers, rotary clubs, and chambers of commerce. While these awards tend to be smaller in monetary value, they are also typically less competitive than national or statewide scholarships.